Image by Riedell
4. This molecule could be joined with others like it to make a
______________________.
PRACTICE SEMESTER TEST- Biology
I
Write answers on a piece of paper then check at the end OR open two
internet windows and keep checking answers at the bottom as you go.
Intro to Biology
Chapters 1 & 2
1. ____________________ would be an example of an autotroph.
2. A water molecule is said to be ___________ because it has an uneven pattern of charge on it.
polar non-polar Organic unicellular
 Image by Riedell |
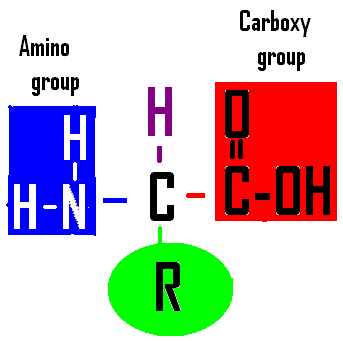
3. This molecule is a(n)
____________________.
4. This molecule could be joined with others like it to make a |
5. The proteins with sugars attached that help cells to "recognize self" are called ________________________
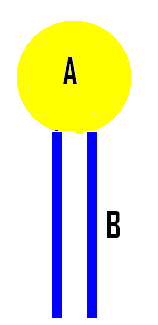 |
6. Which part of this phospholipid molecule is POLAR?
A B |
7. DNA and RNA are ___________________
A. carbohydrates
B. nucleic acids
C. lipids
D. proteins
Cell Structure and Transport
Chapter 7
8. What does a lysosome do?
9. Which of these organelles is missing in
bacteria?
cell membrane
nuclear membrane
cell wall
ribosomes
10. Cells with NO nuclear membrane or membrane bound organelles are called _____________________
prokaryotes eukaryotes
| 11. The function of this organelle is to ________________________ |
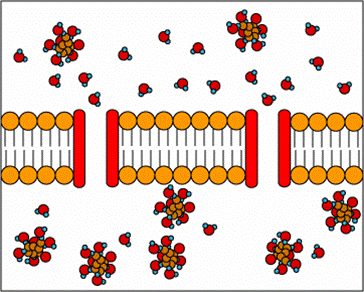 |
12. Name the membrane proteins that help water molecules cross cell membranes. |
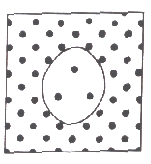 |
13. This diagram shows an animal cell placed in a solution. Black dots represent
solute molecules. The cell in this picture is in a _______tonic solution. |
14. What will happen to the cell above?
It will shrink
It will swell and explode
It will stay the same size
15. The swelling and bursting of an animal cell in a hypotonic solution is called _______________
16. What keeps a plant cell from swelling and bursting?
MITOSIS/MEIOSIS
Chapter 10 & 11-4
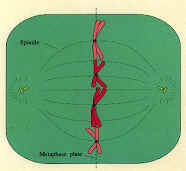 17. This cell is in
____________.
17. This cell is in
____________.
interphase anaphase prophase metaphase telophase
18. The area of an animal cell membrane that pinches in during cytokinesis the ___________________.
19. The phase of the cell cycle which follows G1 phase is
S M C G2
20. Which phase of mitosis could also be called "reverse prophase"?
21. Plant cells undergo cytokinesis by forming a _______________ instead of a cleavage furrow.
22. Type of cell division that produces 2 identical diploid cells.
23. Sperm and eggs are _____________ cells DIPLOID HAPLOID
24. Synapsis, crossing over, and independent assortment are seen in which type of cell division?
Genetics
Chapter 11
25. Tall (T) peas are dominant over short (t) peas.
If you cross homozygous tall
peas with homozygous short peas, what percent of the offspring will be short?
none 25% 50% 100%
26. The "way an organism looks" is its ________________
genotype phenotype
27. Crossing a PURE RED flowered plant with a PURE WHITE flowered plant and getting ALL PINK flowered offspring is a example of _________________
Codominance
Complete dominance
Incomplete dominance
Human genetics
Chapter 14
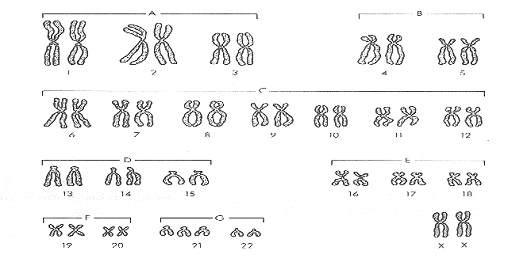
28. The person above has which genetic disorder?
29. Persons with ____________________ can NOT make the protein that helps blood to clot.
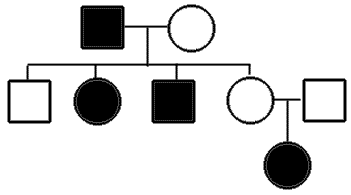
30. The diagram above that is used to show how traits are passed on is called a _________________.
31. _______________ is an example of an X-linked recessive disorder.
Huntington's
hemophilia
cystic fibrosis
Down syndrome
32. Persons who are heterozygous for sickle cell disease have a resistance to which other disease?
DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS
Chapter 12
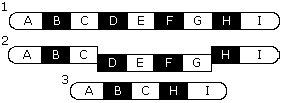 |
33. Name the mutation shown in the picture at the left. |
 Codon wheel from: BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 |
34. Tell
the amino acid sequence coded for by this mRNA
U A C G C A G G U |
|
35. What
do we call the small pieces of DNA that are edited out of the mRNA message
before it is expressed? |
36. Making an RNA message from a sequence of DNA is called _________________
37. Tell the kind of RNA that has an ANTICODON region and is attached to an amino acid.
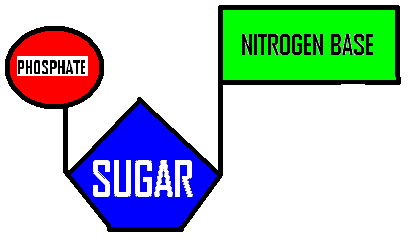 |
38. Name this subunit used to
make nucleic acids.
39. If you were using this to make DNA |
40. Another name for protein synthesis is _______________________
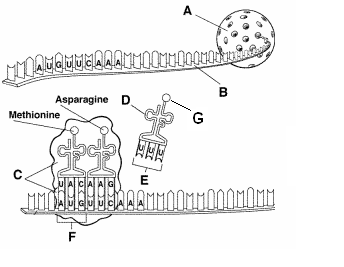 ©Pearson Education Inc; Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall; |
41. E = ?
42. F = ? 43. G = ?
|
1. green plant
2. polar
3. amino acid
4. protein
5. glycoproteins
6. A- the head is polar
7. DNA & RNA are nucleic acids
8. contain digestive enzymes
9. nuclear membrane
10. prokaryotes
11. burn glucose and store energy as ATP
12. aquaporins
13. HYPERtonic
14. It will shrink
15. cytolysis
16. cell wall is sturdy
17. metaphase
18. cleavage furrow
19. S
20. telophase is reverse prophase
21. cell plate
22. mitosis
23. haploid
24. meiosis
25. none will be short/100% will be tall
26. phenotype
27. incomplete dominance
28. Down's syndrome
29. hemophilia
30. pedigree chart
31. hemophilia is X-linked
32. malaria
33. deletion
34. tyrosine-alanine-glycine
35. introns
36. transcription
37. transfer RNA or t-RNA
38. nucleotide
39. deoxyribose
40. translation
41. anticodon
42. codon
43. amino acid
|
Use of our material: All
original materials link are created by We have worked very hard on activities, Powerpoints/games/worksheets, etc to make
this a resource for our students. If you are using our materials, please give us
credit for our efforts by listing us as a source with links to our site. DO NOT
USE these materials for commercial purposes.
PLEASE DO NOT POST ANSWER KEYS FOR OUR
MATERIALS TO OTHER WEBSITES! |