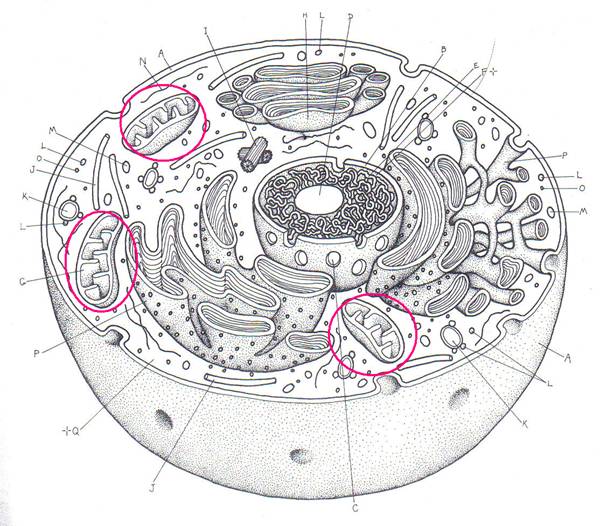
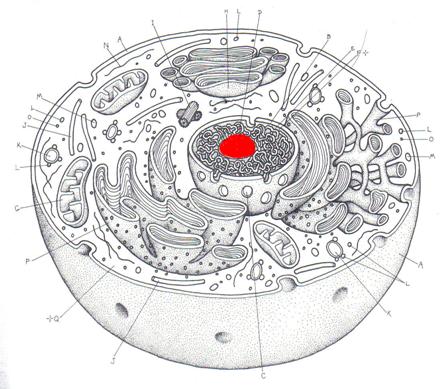
#1.
Name this organelle.
#2.
Give the function for #1.
HONORS BIO-CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND TRANSPORT CARD REVIEW
(We did this in class)
Fill in your answer sheet and check your answers.
 |
#1.
Name this organelle. #2.
Give the function for #1.
|
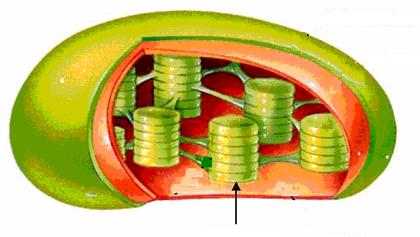 |
#3.These membrane sacs are called _________. |
| #4. Name this integral protein found in cell membranes that helps in cell identification. | 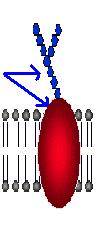 |
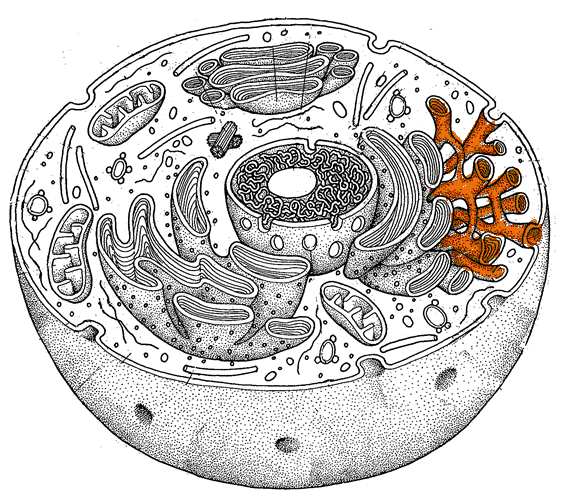 Image modified from: Big Biology Coloring Book |
#5.
Name this organelle. #6.Give a function for #5. |
|
#7. Match the m |
|
| PLANTS
____________________ BACTERIA ___________________ FUNGI _________________________ |
CHITIN CELLULOSE PEPTIDOGLYCAN |
#9.The
folded membranes inside a mitochondrion are called ________.
#10.
The DNA with attached proteins that is SCRUNCHED UP in DIVIDING cells is called
______________
#11.
Name a cell part made from MICROTUBULES
 |
#12. Give the function |
#13.
Ribsomes can be found attached to_____________.
#14.
Membrane proteins that stick into the cell membrane either part way or all the
way through are called
#15.
________________and ___________ are the two main molecules that make up cell
membranes.
#16.
____________ are the smallest kind of cell.
Plant
cells
Animal cells
Bacterial cells
#17.
The gel-like fluid and the organelles it contains which is found inside the cell
membrane is called ____________________.
#18.
An organism with a nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles is called a
_________________.
#19.
Name the 2 organelles BESIDES THE NUCLEUS that have a DOUBLE MEMBRANE AND their
OWN DNA.
| #20. Name an organelle that has this arrangement of microtubules. | 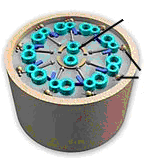 |
#21.
Name a part found in plant cells but not animal or bacterial cells.
#22.
REMEMBER EVERYTHING IS CONNECTED
Trace the path a protein (like insulin) would follow from where it is made to
the exit if it is going to be exported from the cell.
___________
→
_______________→_________________→___________________
#23. Which part acts as the UPS/post office of the cell to sort, modify, and package molecules for transport out of the cell?
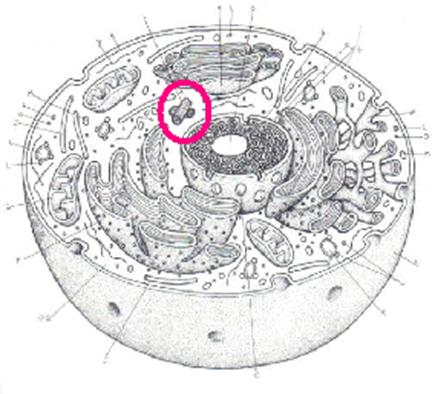 |
#24.
Name this part. #25. Tell what it does. |
#26.
Give an example of an organism that is a EUKARYOTE.
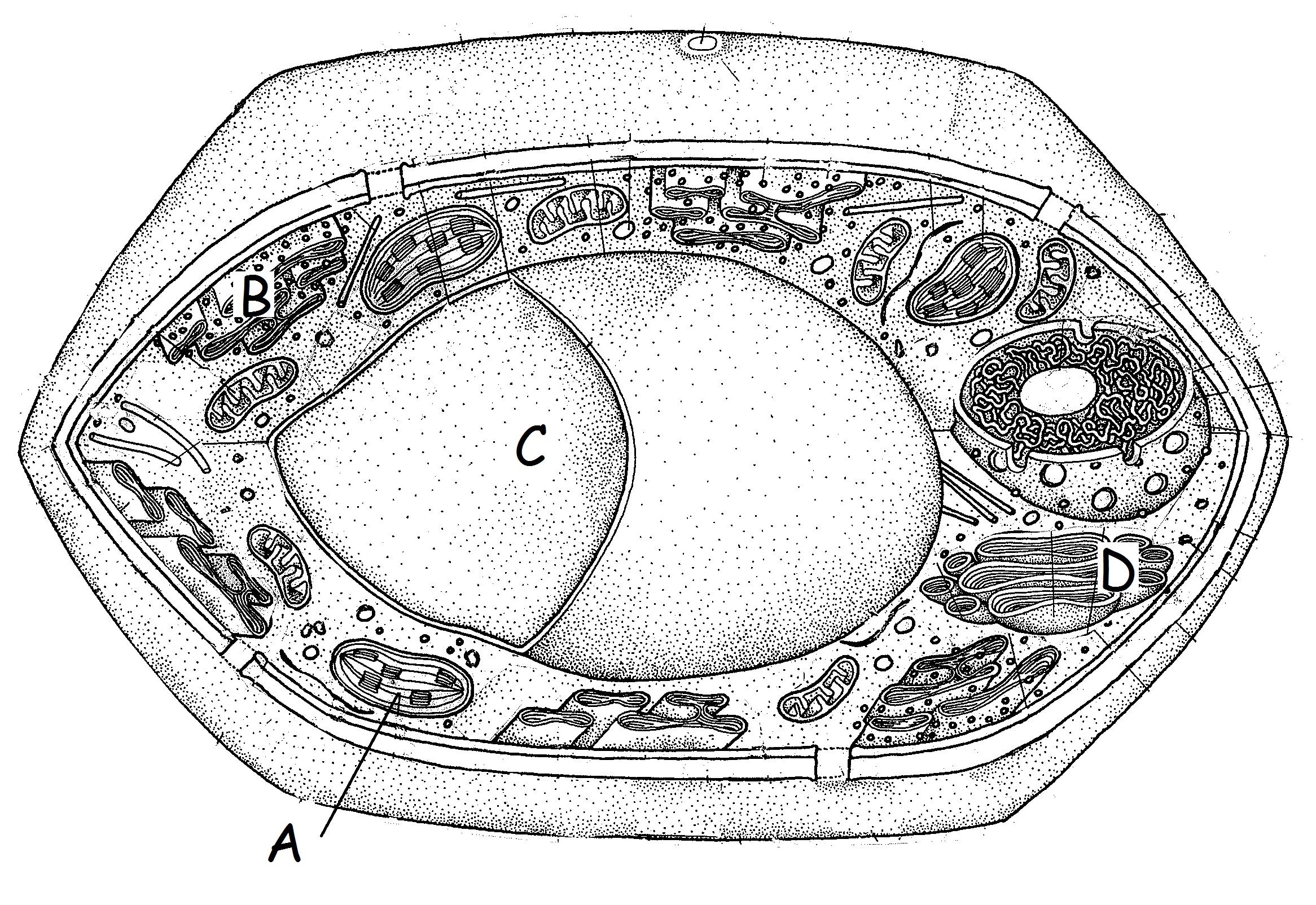 |
#28. Name A. #29. Give its function.
|
|
#30.
Name C #31. Give a function.
|
 |
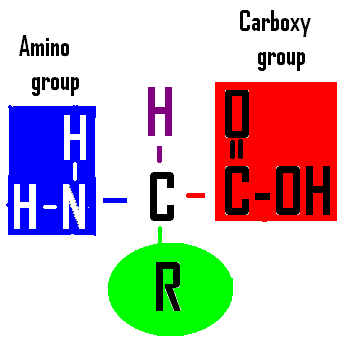 |
#33. Name the cell part that joins subunits like this to make a bigger macromolecule. |
| Match the membranes found inside with the cell part | |
| #35. Mitochondria _________________________ Chloroplasts ____________________________ Golgi bodies _____________________________ |
THYLAKOIDS CISTERNAE CRISTAE |
#36.
When water enters a plant cell the osmotic pressure inside will _______.
increase OR
decrease
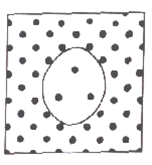 |
#37. The dots in this diagram represent dissolved solute molecules. This diagram represents a cell placed in a ______ solution.
hypotonic
isotonic
hypertonic
#38. The cell in the
diagram will _____.
shrink
swell & burst
stay the same size |
 |
#39
The swelling and possibly bursting of an animal cell when placed
in a HYPOTONIC solution is called _______________.
plasmolysis
cytolysis
crenation |
#40. Membrane proteins that help water molecules move across cell membranes are called ______________________
#41.
The diffusion of WATER from high concentration to LOW concentration
across a semi-permeable membrane is called ______________.
#42.
Molecules will automatically move from an area with _______ concentration
to an area of ________ concentration.
low to high
high to low
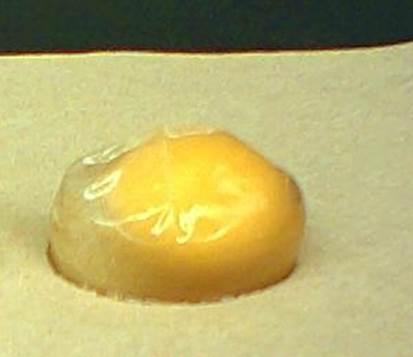 |
44.
This egg lost water because it was placed in a ______ solution.
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
|
#46. The Endosymbiotic theory explains the origin of which TWO cell organelles?
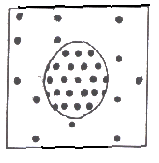 |
#47. The dots in this diagram represent dissolved solute molecules. This diagram represents a cell placed in a ______ solution.
hypotonic
isotonic
hypertonic
#48. The cell in the
diagram will _____.
shrink
swell & burst
stay the same size |
49. Give one example of evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory.
HONORS CELL
PARTS /TRANSPORT REVIEW ANSWERS
1. Mitochondria
2. Powerplant/Burn glucose/make ATP
3. Thylakoids
4. Glycoproteins
5. Smooth ER
6. make lipids,
regulate Ca++ in muscles,
break
down toxins in liver
7. Plants-cellulose
Bacteria- peptidoglycan
Fungi-chitin
8. Selectively permeable OR semi-permeable
9. Cristae
10. Chromosomes
11. Cilia, flagella, cytoskeleton, centrioles
12. Make RNA for ribosomes
13. Rough ER
14. integral
15. Phospholipids + proteins
16. bacterial cell are the smallest
17. cytoplasm
18. eukaryote
19. Mitochondria & Chloroplasts
20. 9 + 2 = Cilia or flagella
21. chloroplasts, really BIG vacuole, cell wall made of cellulose
22. made on ribosomes
→ transported through Rough ER → processed by Golgi body → out
through Plasma membrane
23. Golgi
24.centrioles
25. Guide chromosomes apart during cell division
26. Plant or animal or Fungi
27.
|
ANIMAL |
BACTERIA |
|
Nucleus |
No
nucleus |
|
Have
membrane bound organelles |
No
membrane bound organelles |
|
No
cell wall |
Have
a cell wall |
|
Centrioles |
No
centrioles |
|
Eukaryote |
Prokaryote |
28. chloroplast
29. photosynthesis
30, vacuole
31. storage
32. Cilia- many, short; Flagella- few, long
33. RIBOSOMES use amino acids to make proteins
34. cytoskeleton
35.
MITOCHONDRIA – Cristae
CHLOROPLASTS – thylakoids
GOLGI BODIES – cisternae
36. increase
37. hypertonic
38.
shrink (Solute sucks!)
39. cytolysis
40. aquaporins
41.
osmosis
42
higher to lower
43. It has a cell wall
44. hypertonic
45. membrane proteins and vesicles
46. mitochondria and chloroplasts
47. hypotonic
48. swell & Burst (Solute sucks!)
49.Mitochondria &
chloroplasts:
are only cell parts with double membrane
have phospholipids in inner membranes like bacteria
divide
using binary fission like bacteria
have a single, circular loop of DNA like bacteria