
HONORS MITOSIS CARD REVIEW
Use a blank sheet of paper to answer the ?'s You can check
answers at the end.
1. Name the phase of interphase in which
 |
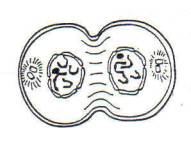
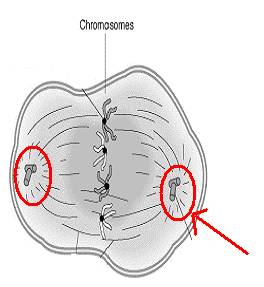
2. Name the phase of mitosis shown here in
which chromatid arms separate and chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. |
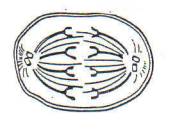
3. Name the phase in which spindle fibers
and centrioles disappear.
|
4. Put the following cells in the correct
order. |
A B C D E |
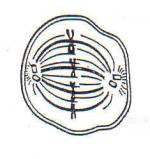
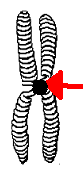
| 5.
Name
this spot that holds the chromatid arms together. |
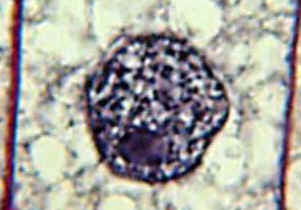
 |
6. DNA
that is spread out in the nucleus of a non-dividing cell is called
_____________.
 |
7.
|
8. Name the phase of the cell cycle in
which cells spend most of their time doing their job.
 |
9. Name
these "log-like" structures that guide the chromosomes
|
10. Name the kind of division used by
bacteria to reproduce.
11. The family of molecules that control
the cell cycle are called __________.
12. Phase of the cell cycle in which the
cell makes molecules and organelles needed for the new cell.
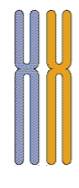 |
13.
Chromosomes that are the same size, same shape, and carry genes for the
same traits are called 14.
True or False
|
15. Name the phase of mitosis that
follows anaphase.
 |
16. Name this phase in which a nucleus
and nucleolus are
visible
|
17. Name the cell organelle responsible
for building the cell plate during cytokinesis in a plant cell.
18. TRUE or FALSE
The chromatid arms on a chromosome are identical.
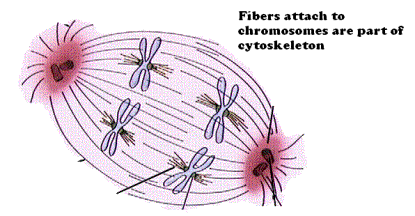 |
19. These microtubule fibers that pull the chromosomes are called the ______________ |
20. Phase of the cell cycle in which
cells stop dividing.
21.
22. Phase in which the nuclear membrane
and nucleolus disappear and spindle fibers and centrioles appear.
23. The centrioles lie in a region called
the __________ which helps to organize the spindle fibers.
24. A disorder in which some of the body’s cells lose the ability to control their cell cycle.
25. The major check point that determines whether a cell will keep doing its job OR move into cell division is found in which phase?
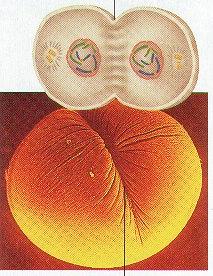 |
26. Tell how you can tell this is an animal cell and NOT a plant cell. |
27.
Phase of the cell cycle in which the nuclear membrane and nucleolus
return.
28. Name the 3 phases that make up
interphase.
29. Phase in which the cytoplasm splits.
30. Phase in which chromosomes spread
back out
into chromatin.
31. Cancer cells have high levels of telomerase enzyme which allow them to do
what?
 |
32. What is this dividing wall called? |
33. The protective tips on the ends of chromosomes are called
_____________________
34. Mutations in the p53gene can lead to what disease?
35.
36. What happens to telomeres as cells age?
MITOSIS REVIEW ANSWERS:
1. S-synthesis
2. anaphase (apart)
3. Telophase
4. A, C, E, D, B
5. Centromere
6. Chromatin
7. metaphase (middle)
8. G1
9. Centrioles
10. binary fission
11. cyclins
12. G2
13. homologous
14. False; similar but not identical
15. telophase
16. Interphase
17. Golgi bodies
18. TRUE chromatids are identical
19. spindle
20. G0
21. S
22. prophase
23. Centrosome
24. cancer
25. G1
26. It has a cleavage furrow; plants don't pinch
27. telophase
28. G1, S, G2
29. cytokinesis
30. telophase
31. Add telomeres back onto their chromosomes so they can divide forever
32. Cell plate
33. telomeres
34. cancer
35. SA/vol ratio gets smaller as cells get bigger
36. Get shorter