
1.
Making a copy of DNA is called _________________________.
2.
Which nitrogen base isn’t used during
3. Name the enzyme you learned about that adds the complementary nucleotides and spell checks to make sure the new copy is correct.
DNA, RNA, & PROTEINS REVIEW
(We did this one in class)
 |
1.
Making a copy of DNA is called _________________________.
2.
Which nitrogen base isn’t used during 3. Name the enzyme you learned about that adds the complementary nucleotides and spell checks to make sure the new copy is correct. |
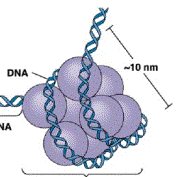
4.
The beadlike bundles that form when DNA wraps up are called _________________.
5.
Name the protein in the center of the bundle that DNA wraps around.
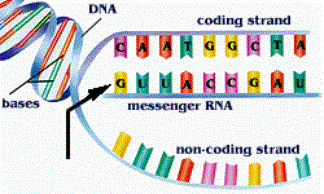
|
|
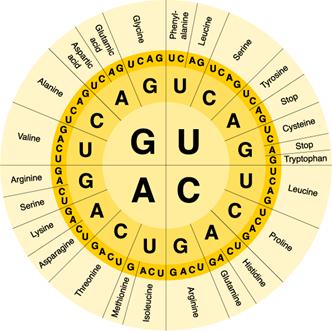 |
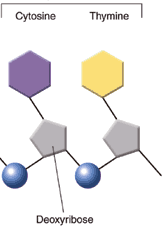
8.
USE THE mRNA CODE WHEEL
Image from:
Biology; Miller and Levine; Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall; 2006
|
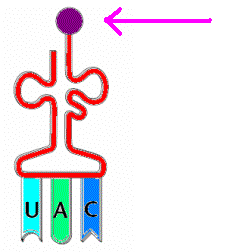
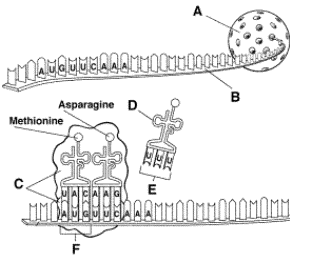
9.
Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON region and carries the amino acids to the
ribosome?
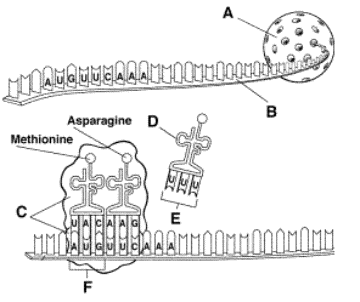 |
10.
B = ? 11.
F = ? 12.
C = ?
|
13.
Tell one way DNA is different from RNA.
14. Tell
the enzyme that adds the nitrogen bases when making an RNA message from DNA.
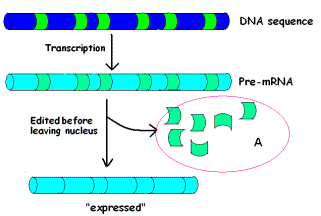 Image by Riedell |
15.
What do we call the small pieces of RNA that are edited out of the mRNA message
before it is expressed? |
16.
DNA that is SPREAD OUT in the nucleus of NON-DIVIDING cells is called
________________.
17.
When making DNA, CYTOSINE always pairs with _______________________.
18.
Using an RNA message to make a protein is called _______________________.
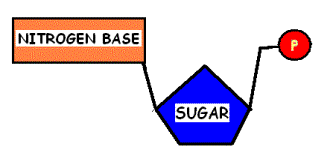 Image by Riedell |
19.
Name this subunit used to build DNA
and RNA. |
 Image by Riedell |
20 The parts of the message that are NOT edited out and end up in the final message are called ___________. |
21.Tell the complementary DNA strand for the DNA sequence shown below
A T T G C C A G C
 |
22.
NAME THIS KIND OF RNA. 23. Name the molecule attached at the arrow. Image modified from: Biology; Miller and Levine; Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall; 2006 |
 |
24. The blender experiment
conducted by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase using bacteriophages showed that _______________
A. pneumonia kills mice
B. Proteins carry the genetic code
C. DNA can be transferred between bacteria
D. DNA carries the genetic code
|
Image from: http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chase_&_Hershey_1953.jpg
25.
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS could also be called ___________________.
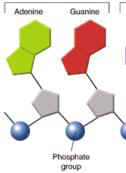 |
26.
Nitrogen bases made up of TWO RINGS are called
________________
|
27.
The process in which one bacteria is changed by the transfer of genetic material
from another bacteria is called _________________.
 |
28.
Nitrogen bases made up of ONE RING are called
________________
|
29.Where
in the cell does translation take place?
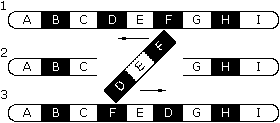
Image from: http://www.biologyonline.org/2/8_mutations.htm
|
30.
Name this kind of mutation. |
31. TRUE OR FALSE:
ALL MUTATIONS ARE HARMFUL.
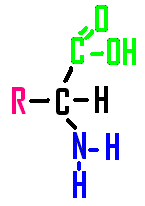
Image by Riedell |
32.
Name this subunit used to build PROTEINS. |
Image
from:
Biology; Miller and Levine; Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall; 2006 |
33.A=? 34. D = ? 35.E = ? |
36.
Name the double stranded nucleic acid
that does not contain URACIL .
37. Name the woman whose X-ray images of DNA helped James Watson and Francis Crick to figure out the structure of DNA.

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rosalind_Franklin |

http://www.time.com/time/time100/scientist/profile/watsoncrick.html |
 |
39. In a DNA molecule, which two parts of the
nucleotide make up the SIDES OF THE LADDER? 40. What kind of bond holds the nitrogen bases
together in the middle? |
41. In a DNA molecule ADENINE always pairs up with
_______________
42. Which of the following sequences show how
information is passed on in cells?
A. RNA
→
PROTEIN →
DNA→
TRAIT
B. PROTEIN
→
DNA →
TRAIT →
RNA
C. DNA
→
RNA →
PROTEIN →
TRAIT
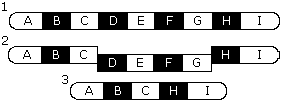 |
43. Name the kind of mutation shown in the diagram at the left. |
44. The place on the DNA where RNA polymerase attaches
and starts reading the information is called the ________________.
45. __________________ are sometimes called “jumping
genes” and are involved in increasing mutation rates when an organism is
stressed.
 |
46. The two strands in a DNA molecule are
called _____________ because they run in opposite directions.
|
47. ______________ mutations are caused by adding or
deleting bases that are NOT multiples of three and causing the reading frame to
regroup and be read incorrectly.
48. When this type of mutation happens at the____________ of a gene it
causes more damage and changes more of the protein.
end beginning
1.replication
2. uracil
3. DNA polymerase
4. nucleosome
5. histone
6. transcription
7. in nucleus
8. serine-lysine-phenylalanine
9. tRNA
10. mRNA
11. codon
12. ribosome
13.
|
DNA |
RNA |
14. RNA polymerase
15. introns
16. chromatin
17. guanine
18. translation
19. nucleotide
20. exons
21. T A A C G G T C G
22. tRNA
23. amino acid
24. D- DNA carries the genetic code
25. translation
26. purines
27. transformation
28. pyrimidines
29. On ribosomes in cytoplasm
30. inversion
31. False; mutations that increase survival and reproduction can be helpful
32. Amino acid
33. nucleus
34. t-RNA
35. anticodon
36. DNA
37. Rosalind Franklin
38. RNA polymerase
39. phosphate and sugar
40. Hydrogen bonds
41. Thymine
42. C -DNA
→ RNA
→
PROTEIN
→
TRAIT
43. deletion
44. Promoter
45. Transposons
46. Antiparallel
47. frameshift
48. Beginning
.