 |
2.
These are examples of ________________ structures because they come from
the same embryonic tissue. |
HONORS EVOLUTION CARD REVIEW
1. Name the
two geologists whose ideas about the age of the earth and processes that shaped
it influenced Darwin.

2.
These are examples of ________________ structures because they come from
the same embryonic tissue.
3. Name 5
kinds of evidence that support Darwin’s Theory of Evolution. (We talked about
more than 5)

4. Breeding
cows that give the most milk or the fastest horses is an example of
__________ ___________
5. Darwin’s
idea that each living species has DESCENDED WITH CHANGES from other species over
time is called __________ ______
___________
6. The
ability of an organism to SURVIVE AND REPRODUCE in its environment is called
__________.
 7.
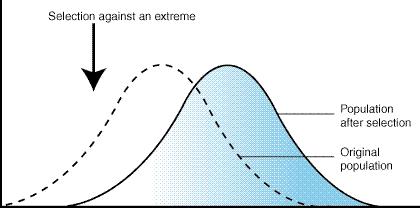
Lamarck proposed that organisms could alter the size or shape of their bodies
through use or disuse and pass these traits on to their offspring.
7.
Lamarck proposed that organisms could alter the size or shape of their bodies
through use or disuse and pass these traits on to their offspring.
This idea is called
________ ___
_________ ______.
8. EXPLAIN
why he was incorrect.
   |
9.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS like walrus tusks & porcupine quills or
BEHAVIORAL CHARACTERISTICS like hibernating & living in herds are
examples of inherited traits that help an organism to SURVIVE AND
REPRODUCE in its environment called ________ |
10. In
addition to observing living organisms, Darwin studied the preserved remains of
ancient organisms called ____________________.
11. Name the
island where Darwin observed finches, iguanas, and turtles that led to his
Theory of Evolution.
12.
A well-supported testable explanation
of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world
is called a ______________.
13. The
process in which organisms that are better suited to their environment survive
and reproduce is called ________________ ____ ____ ___________.
14. Which of
the following is NOT part of
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution?
A. Organisms in a population show a natural variation in heritable traits.
B. Organisms must compete for resources because organisms produce more offspring
than can survive.
C. Individuals best suited to their environment will survive and reproduce most
successfully passing on their traits.
D. Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species
that lived in the distant past.
E. Evolution unites all organisms into a single “tree of life”
F. Acquired traits can be inherited.
15.
________________ organs like hipbones in snakes are reduced in size and no
longer functional.
16. Give an
example of #15.
17. Name the
naturalist whose ideas about evolution were similar to Darwin’s and who prompted
Darwin to publish his book “On the Origin of Species”.
18. Whales
and wolves share a common ancestor but don’t look anything alike. This is an
example of __________________ evolution.
19. Whales
and sharks are not closely related but have similar body shapes.
This is an example of __________________ evolution.
20. Tell one
reason why human chromosome #2 suggests a relationship between humans and
chimpanzees.
21. Genes that have mutated so they are no longer functional are called
_____________.
22. Name the
5 conditions required to maintain genetic equilibrium under the HARDY-WEINBERG
PRINCIPLE.
23. If a
population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium then evolution
____________ happen.
does does not
24. TRUE OR FALSE Most of the time
in most populations the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg DO NOT ALL EXIST.
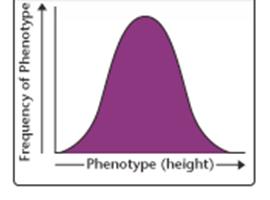 |
25.
______________traits are determined by more than one gene and show this
kind of distribution (like lima bean length, human intelligence, or skin
color) |
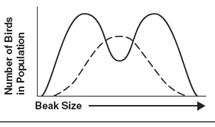
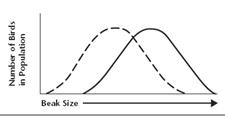
26. Match
the kind of selection with the graph shown below
 |
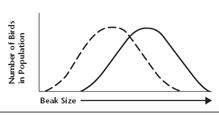 |
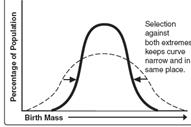 |
|
| A | B | C |
27. In
genetic terms, ________________ is a change in the relative frequency of alleles
in a population.
 |
28.
Name the pattern of macroevolution in which two organisms evolve in
response to changes in each other (like flowers and their pollinators) |
29. The
process by which organisms with different recent ancestors change to become more
alike because they live in the same kind of environment is called
_____________________ evolution
convergent divergent
 30.
Name the pattern of macroevolution in which populations show a pattern of long
stable periods interrupted by brief periods of rapid change.
30.
Name the pattern of macroevolution in which populations show a pattern of long
stable periods interrupted by brief periods of rapid change.
31. Name the
two mathematicians who came up with an equation to show the allele frequencies
in a population and describe evolution in populations.
32. Another
name for divergent evolution is ______________
_______________.
33. The
process by which organisms that share recent common ancestors change to become
different is called _________________________ evolution.
convergent
divergent
34. Darwin
believed that evolution HAPPENED SLOWLY OVER A LONG PERIOD OF TIME called
_______________
35. Evidence
suggests that at the end of the Cretaceous period an asteroid hit the Earth
causing the loss of many species including the dinosaurs. This is an example of
what pattern of evolution?
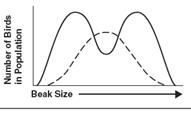
36. A
population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are
wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would
have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population
splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds and one that eats large
seeds.
This is an example of _______________ selection.
Disruptive
Directional Stabilizing
37. In
birds, feather color among males is more likely to attract a mate, but also more
likely to attract a predator. Over
time and many generations, the highest frequency color is for males with medium
colors, while males with very dull colors and males with very bright colors
became increasingly rare. This is an example of ________________ selection.
Disruptive
Directional Stabilizing
38. The last
test in Biology class was extremely hard. A graph of the scores shows a bell
shaped curve with the average score being a 68% D. The teacher curves the test
scores so that the new class average is a 77% C. The graph that shows this
change in the grading scale would look similar to a graph showing which kind of
selection?
 |
 |
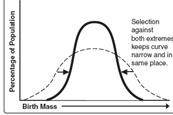 |
| Disruptive | Directional |
Stabilizing |
1. HUTTON & LYELL
2. HOMOLOGOUS
3.
Artificial selections works, Fossils,
DNA/molecule
Geographic distribution, Antibiotic resistance,
homologous
structures/vestigial organs,
embryology, pseudogenes, human chromosome #2
new diseases (AIDS, bird flu), see it happen
4. Artificial selection
5. descent with modification
6. Fitness
7. inheritance of acquired traits
8. only traits in genes are passed on
9. adaptations
10. fossils
11. Galapagos
12. theory
13. survival of the fittest
14. F
15. vestigial
16. hipbones in whales/snakes, skink legs,
appendix in humans
17.
Alfred Wallace
18. divergent evolution (adaptive radiation)
19. convergent evolution
20 . Banding pattern matches, telomeres in
middle where not supposed to be, extra inactive centromere
21. pseudogenes
22. Large population, random mating,
no
mutations, no movement in or out,
24.TRUE
25. Polygenic
26. A-disruptive
B-Directional
27. evolution
28. coevolution
29. convergent
30. Punctuated equilibrium
32. Adaptive radiation
33. divergent
34. gradualism
35. Mass extinction
36. disruptive
|
|