
http://0.tqn.com/d/webclipart/1/0/f/U/2/msh91.gif
http://szuperblog.hu/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/Cow.gif
http://systemaxonline.com/clipart/cartoons/lion1.gif
BIOSPHERE
CARD REVIEW (We did this in class)
Fill in your answer sheet, then check answers at end.
1. Name the 3 kinds of symbiosis you learned about.
2. Name one
way CARBON is added to the atmosphere during the carbon cycle.
3. Name TWO
of the FOUR ways you learned about that organisms interact in an ecosystem.
4. Food
chains always have a(n)______________ on their first trophic level.
5.
Process in which bacteria convert
nitrates into nitrogen gas and release it into the atmosphere.
6. Which of
these is a decomposer?
7. The process
in which water from plant leaves evaporates into the atmosphere is
_______________.
8. Name the
biogeochemical cycle you learned about that does not cycle through the
atmosphere.
9. Which of
the following is NOT part of the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification Nitrogen
fixation Photosynthesis
Addition of fertilizer
Waste excretion by animals
10. TRUE OR
FALSE Humans get the nitrogen they need from the atmosphere.
11. Which of
these is a herbivore?
12. Name a biomolecule found in living things that contains NITROGEN.
13. The water cycle is also called the _______________ cycle.
 |
14. Name this kind of symbiosis shown
between bees and flowers.
|
15. Make a food chain out of the following:
herbivore
omnivore
producer
16. Name the biogeochemical cycle that includes:
run off, precipitation, evaporation,
transpiration, and condensation,
17.
Put the
following in order of increasing complexity.
biosphere
population
organism ecosystem
community
biome
18. Bacteria
in the soil that have a symbiotic relationship with legumes can turn nitrogen
gas into ____________ in a process called nitrogen fixation.
19. Type of symbiosis in which one organism benefits but the other is neither
helped nor harmed.
20.
Name THREE of the FOUR biogeochemical cycles you learned about.
21. Name
something organisms have to compete for in an ecosystem.
22. An
organismís ___________ describes where it lives, what it eats, what eats it, how
it interacts with other organisms, how and when it reproduces, and how it acts.
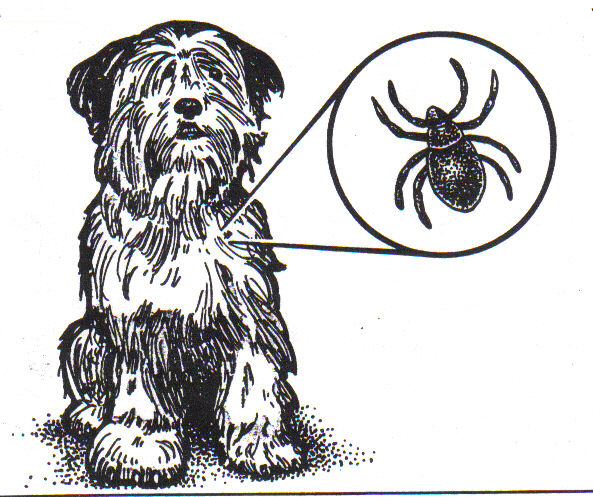 |
23.
Name this type of symbiosis. |
24. Which
organisms are necessary for producing ammonia, nitrates, and nitrites during the
nitrogen cycle?
25.
All the non-living things in an
ecosystem that affect an organism
are called ___________ factors.
26. Some
bacteria that live in hostile places (like volcano vents) can produce their own
food WITHOUT LIGHT in a process called _________________
27. Organisms that feed on dead plant &
animal remains are called ____________________.
28.
Each step in a food chain or web
is called a ___________ level.
29.
A ______________ is anything needed by an organism for life.
30. A
nutrient that is in short supply or that cycles slowly which limits population
growth is called a ____________________.
31. Which
biogeochemical cycle includes a reservoir underground stored as fossil fuels?
32.
_____________ is the process in which water vapor turns back into
liquid form.
33. Name the type of symbiosis between legumes and nitrogen fixing bacteria.
34.
The
__________________ principle states that no two species can share the same niche
at the same time.
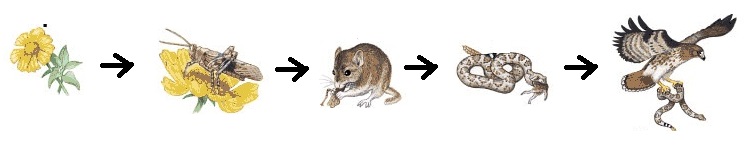 |
| 35. In this food chain,
the mouse is a ____________________ consumer. 36. In this ecosystem, which population of consumers would be the largest?
|
37. Tell how
a detritivore is different from a decomposer.
38. Tell the
group of organisms that the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles have in
common that keep matter cycling between the living and nonliving parts of an
ecosystem.
39.
40. In which
process do plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere during the carbon
cycle?
 |
|
1. mutualism
Commensalism
Parasitism
2. burning
fossil fuels
Volcanic activity
respiration
decomposition of dead matter
3. competition
Predation
Cooperation
Symbiosis
4. producer/autotroph
5. denitrification
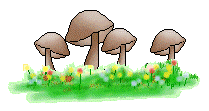
6. mushroom (fungi)
7. transpiration
8. phosphorus cycle
9.
photosynthesis
10. false; from food
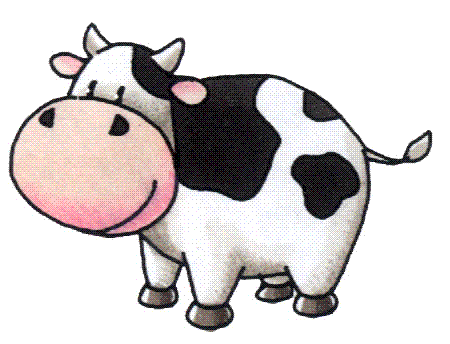
11. cow
12. proteins, amino acids, DNA, RNA, ATP
13.
hydrologic
14.
mutualism
15.
producer → herbivore →
omnivore
16. water
(hydrologic)
17.
organism→ population →
community → ecosystem →
biome → biosphere
18. ammonia
19. Commensalism
20. carbon, nitrogen,
phosphorus,
water
21. food,
shelter,territory/space, light, water, mates
22. niche
23. parasitism
24.
bacteria
25. abiotic
26. chemosynthesis
31. Carbon cycle
35.
Secondary consumer
36.
grasshoppers; each level has to be
37. Detrivores eat with mouth; decomposers absorb through surface
40.
photosynthesis
41. carrying capacity