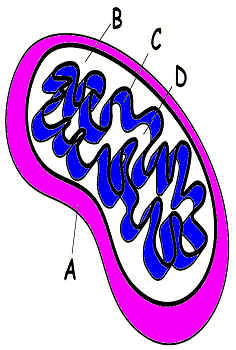
 E
EImage modified from:
Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall © 2006
#2. A = ?
#3.
B
#4.
C = ?
#5.
D
#6. E = ?
Cellular Respiration Review
Use paper and pencil or fill in
answersheet to answer the questions. You can check your answers at
the end.
#1.
Name the molecule that acts as the last electron acceptor for electrons moving
down the Electron Transport Chain during Cellular Respiration.
 E EImage modified from: Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall © 2006 |
#2. A = ?
#3.
B
#4.
C = ?
#5.
D #6. E = ? |
#7.
Name the 3 pathways that make up cellular respiration.
#8.
Name the 2 pathways that pyruvic acid might follow if oxygen is NOT available.
#9.
Name the TWO high energy electron carriers used during cellular respiration.
#10.
Write the equation for cellular respiration.
#11.
How is this related to the equation for photosynthesis?
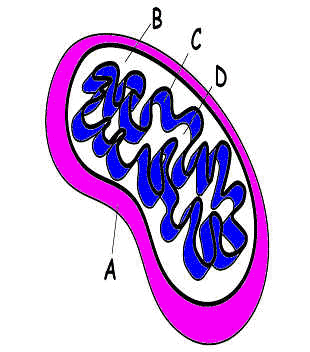 Image modified from: Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall © 2006 |
#12.
Which of these is the place
where H+ ions build up during Electron
Transport?
#13.
Which of these is the place where the
Electron Transport chain is
located?
#14.
Which of these is the place where the Krebs cycle happens? |
#15.
Name the enzyme that spins as H+ ions pass through it providing
energy to add a phosphate group to ADP.
#16.
Write the equation for alcoholic fermentation.
#17.
Which of these processes DOES NOT use alcoholic fermentation?
A. yeast making beer
B. bacteria making wine
C. yeast making bread rise
D. bacteria making cheese or yogurt
#18. How many ATP’s are produced from 1 glucose molecule completing cellular respiration ?
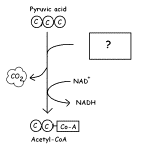
|
#19.
Name this missing ? molecule. #20.
Where will this Acetyl-CoA molecule go next?
|
#21.
Name the 3 carbon molecule that forms when glucose is split in half during
glycolysis.
#22.
What is the relationship between calories and Calories?
#23.
Name the 6 carbon molecule that forms during the first step of the Krebs cycle.
#24.
Fermentation is said to be ________________ because it happens “NOT IN AIR”
or without oxygen.
25.
Compare NADH and FADH2 in terms of their ability to produce ATP’s
using the electron transport chain.
#26.
Name the pathway used by muscle cells during short vigorous exercise like the 50
yard dash.
#27.
How many NET ATP’s are produced using glycolysis and lactic acid fermentation?
#28.
What happens to the NADH molecules produced during glycolysis?
#29.
What decides which pathway pyruvic acid
follows
after glycolysis?
#30.
Where do the 6 carbons in glucose end up following cellular respiration?
#31.
Which molecule is regenerated during fermentation that allows cells without
oxygen to continue to make ATP using glycolysis?
#32.
Which stage of cellular respiration generates the most ATP molecules?
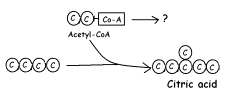
|
#33.
What happens to Coenzyme A (Co-A) once Acetyl-CoA reacts to form citric acid? |
#34.
Tell the products of cellular respiration.
#35.
Name the two molecules you learned about that can be burned for energy during
extended exercise when glucose runs out.
1.
oxygen
2.
outer membrane
3.
intermembrane space
4.
inner membrane
5. matrix
6. cytoplasm
7.
glycolysis, Krebs cycle,Electron Transport chain
8.
alcoholic or lactic acid
fermentation
9. NADH
or FADH2
10.
C6H12O6+ 6 O2
→
6 CO2
+ 6 H2O +
energy
11.opposite
of photosynthesis
12. B
13. C
14. D
15. ATP synthase
16.
Pyruvic acid
+
NADH
→alcohol
+ CO2+ NAD+
17.
D.
making cheese uses lactic acid fermentation
18.
36
19. Co-enzyme A
(Co-A)
20. go into Krebs cycle
21. pyruvic acid
(pyruvate)
22. 1 Calorie = 1000 calories
23. citric acid
24. anaerobic
25.
1 NADH makes 3 ATP; 1 FADH2 makes 2 ATP
26.
lactic acid fermentation
27. lactic acid fermentation makes 2 ATP
28.Go
to Electron transport
29. presence
of oxygen
30.
given off as CO2
31.
need to regenerate NAD+
32.
Electron Transport Chain
33.
recycles to pick up a
34.
CO2 and H2O
35.
glycogen
and
fat