AP
BIO GENETICS CARD REVIEW (Chapter 14 & 15)
Fill in your answer sheet and check answers at end.
 |
 |
1.
Identify the genotype for individual 6.
2. Identify the genotype for individual 1.
3. Identify the genotype for individual 9.
4. Which of the following disorders is X-linked?
A. Tay-Sachs
B. Cystic fibrosis
C. Hemophilia
D. Albinism
E. Huntington’s disease
5. A court case is trying to determine the father of a baby. The mother has type
O blood, and the baby has type B. Which of the following blood types would mean
that a man is definitely NOT the father of the baby?
A
B
AB
O
Can’t tell any could be
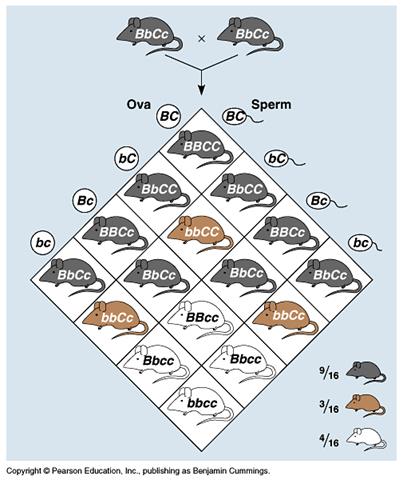
6. From a cross of AABbCc with AaBbCc, what is the probability that the
offspring will display a genotype of
AaBbCC?
7. Imagine that in squirrels gray color (G) is dominant over black color (g). A
black squirrel has the genotype gg.
Crossing a grey squirrel with which of the following would let you know for
certain the genotype of the grey squirrel?
A. GG
B. Gg
C. gg
8. Name 2 disorders that are autosomal recessive disorders.
 |
9. This pedigree can be explained by all of the
following inheritance patterns EXCEPT: A. autosomal dominant allele B. autosomal recessive allele C. X-linked dominant allele D. X-linked recessive allele E. Y-linked trait |
|
10. The following crossover frequencies were noted
via experimentation for the 5 genes on a single chromosome. A-B- 35 % B-C- 15% A-C- 20% A-D- 10% D-B- 25% A-E - 5% B-E - 40% |
 |
11. If C and D are linked genes with a crossover frequency of 50%, which of the
following is true for sperm from an individual with the genotype CcDd?
A. all CcDd
B. ¼ CCDD + ½ CcDd + ¼ ccdd
C. ½ Cc + ½ Dd
D. ½ CD + ½ cd
E. ¼ CD + ¼ Cd + ¼ cD + ¼ cd
12. Use the following pea gene codes:
Y = Yellow
y=green
R = round
r = wrinkled
If two parents, both green and round are crossed and the offspring are ¾ green
and round and ¼ green and wrinkled, what are the genotypes of the parents?
A. YyRr
B. Yyrr
C. yyRR
D. yyRr
E. yyrr
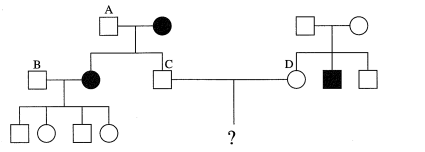 |
This pedigree show an AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE
trait. 13. What is the genotype of person A? A. Bb B. BB C. bb D. Cannot be determined from the given information. 14. What is the most likely genotype of person B? A. Bb B. BB C. bb D. Cannot be determined from the give information. |
15.
If a trait is ______________ (like male pattern baldness or milk production in
mammals) the same genotype can show as different phenotypes in males or females.
16. In fruit flies, white eyes are a sex-linked recessive characteristic. If a
white-eyed female is crossed with a wild-type male, what proportion of the male
offspring should have white eyes?
17. The differences seen in children with Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman’s
syndrome who each have the same deletion on chromosome 15 but show different
phenotypes are due to ______________.
Epistasis
Genomic imprinting
Pleiotropy Incomplete
dominance
18.
A family has 5 children and all are sons. If they have another baby what is the
probability that it will be a girl?




 ?
?
19. What is the probability that this family has 6 children and they ARE ALL
SONS?






20. Which genetic disorder could be
diagnosed by looking at a person’s karyotype?
PKU
Tay-sachs
Huntington’s
hemophilia
Down syndrome
 |
21. ______________
occurs
when a single gene influences multiple phenotypic traits |
22. We are learning more about a new branch of genetics called epigenetics which
deals with how genes are regulated.
Adding ____________ tags to cytosines in DNA “turns genes” ______.
name the functional group
ON
OFF
|
A male fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) with red eyes and long
wings was mated with a female with purple eyes and vestigial wings. All
of the offspring in the F1, generation had red eyes and long
wings. These F1 flies were test crossed with purple-eyed,
vestigial-winged flies. Their offspring, the F2 generation,
appeared as indicated below.
F2 Generation:
125 red eyes, long
wings
124 purple eyes,
vestigial wings
18 purple eyes, long
wings
16 red eyes,
vestigial wings
283 Total |
23. What do these results tell you about these two genes?
24. Calculate the crossover frequency.
25. Draw a map to show the location of these two genes.
 |
EX: Coat color in mice
B = Black
|
| 26. ________________ occurs when a
gene at one locus
alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at another locus. |
|
27. People who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele have what is called a
“heterozygote advantage”. What advantage do they have?
28. Give an example of an AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT disorder you learned about.
29. Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis is called
____________________.
30. Name a genetic disorder you learned about that could be a result of this
happening.
31. X-linked recessive genetic disorders show up more frequently in which
sex?
EXPLAIN WHY.
32. Which genetic disorder you learned about shows up more frequently in people
with Jewish or Middle Eastern ancestry?
33. Name the cell part that is nonfunctional in Tay-Sachs and PKU.
34. If genes A, B, C, and D are unlinked and autosomal, what is the probability
of producing an individual with the genotype AABbccDd from this cross:
AaBbCcDd X AaBbCcDd
35. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is an X-linked recessive trait that results in
muscle deterioration. Death usually occurs before puberty. Assuming that no
individual with the disease reaches puberty and passes on their gene to the next
generation, how can the appearance of the disease be explained in females?
A. Affected females are homozygous recessive for the Duchenne allele.
B. Affected females are homozygous dominant for the Duchenne allele.
C. In females heterozygous for the Duchenne MD, both alleles are expressed in
muscle cells.
D. In females heterozygous for Duchenne MD, X-inactivation in muscle cells of
the chromosome with the normal allele allows expression of the disease.
E. The disease cannot occur in females
ANSWERS
GENETICS CARD REVIEW ANSWERS
1. E
2. B
3. C
4. C-hemophilia
5. If mom is O, baby’s B came from
dad. Dad can’t be A or O
blood type.
6. ½ x ½ x ¼
= 1/16
7. Test cross with C-gg
8. Tay-Sachs, Cystic fibrosis, PKU
9. C - Xlinked dominant
10. A.
E-A-D-C-B
11. E. sperm are haploid/need one of each letter
12. D if green , both gotta be yy
13. A- Bb
14. B – BB
15. SEX INFLUENCED (on autosome) but shows differently in males and females
16. 100% of males will have white eyed; 100% of females will have red eyes
17. Genomic imprinting
18. ½
19. ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/64
20. Down syndrome; can’t see single gene mutations in a karyotype
21. Pleiotropy
22. Methyl tags attach to cytosine in DNA and turn off genes
23. Genes are linked
24. 34/283 = 12%
25. Eye color and wings are 12 map units
apart
26.epistasis
27. Malaria resistance
28. Huntington’s, achondroplasia
29.nondisjunction
30. Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Xyy, XXX
31. Males; males don’t have a back up X (no copilot) to cover the mutation;
girls have 2 X’s so if one has the mutation they have another X to cover for
them.
32. Tay-Sachs
33. Lysosomes
34. ¼ X ½ X ¼ x ½ = 1/64
35. D