13. Which of these diagrams represents a chemical reaction with a +∆G ?
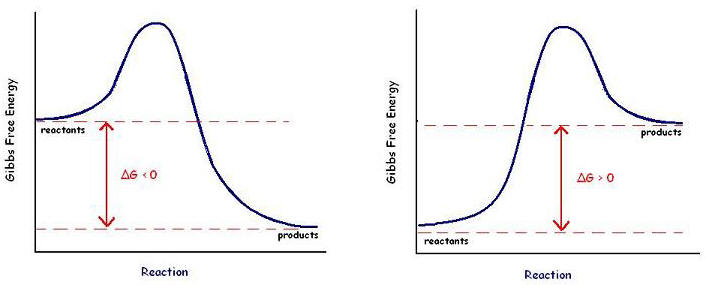
A B
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikibooks/en/a/a6/Gibbs_free_energy.JPG
METABOLISM CARD REVIEW
1. During the light
dependent reactions where do H+ ions accumulate?
2. What are the TWO
sources of these H+ ions?
3. During photosynthesis, which molecule acts as the final electron acceptor at
the end of the electron transport chain?
4. Write the overall
equation for cellular respiration.
5. How does this compare to the equation for photosynthesis?
6. Which color
wavelength(s) of light do/does chlorophyll absorb best?
7. In which kind of
plants (C3, C4, CAM) would you find bundle sheath cells?
8. Give an example of a C4
plant?
9. C4 and CAM
plants have evolutionary adaptations that allow them to do what?
10. Why do plants switch
to cyclic rather than noncyclic photophosphorylation?
11. Where does the oxygen
that ends up in glucose during the Calvin cycle originally come from?
12. What are the products
of the light dependent reaction?
|
13. Which of these diagrams represents a chemical reaction with a +∆G ?
|
 A B http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikibooks/en/a/a6/Gibbs_free_energy.JPG |
14. What is energy coupling and how do cells use it?
15. NONCOMPETITIVE enzyme inhibitors bind to the __________ site on an enzyme.
active
allosteric
16. If oxygen is low or
unavailable what pathway do cells use to obtain energy?
17. Which electron
carrier produces the most ATP when it passes its electrons through electron
transport in the mitochondria?
18. Compare the
production of ATP during the 3 stages of cellular respiration.
19. What determines
whether a cell does fermentation or switches into Krebs cycle?
20. Name the two types of
fermentation and give example of an organism that uses each kind.
21. Cells can get ATP
from doing glycolysis. Continuing on into fermentation produces no additional
energy. For what reason do cells do fermentation?
22. What is the electron
acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain in mitochondria?
23. Where do the
carbons from glucose end up following the Krebs cycle?
24. Another name for the
Krebs cycle is _________________.
25.
Explain the effect of temperature on an enzyme catalyzed reaction.
26. Tell the molecule
that the carbon from CO2 is added to during carbon fixation in C4
and CAM plants.
27. Which bonds are
disrupted in an enzyme when it denatures?
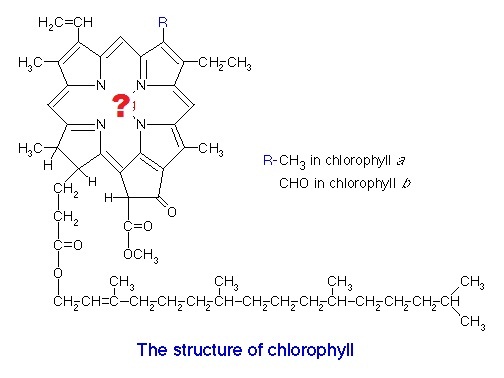 http://chaitanya1.files.wordpress.com/2007/07/chlorophyll.gif |
|
29.
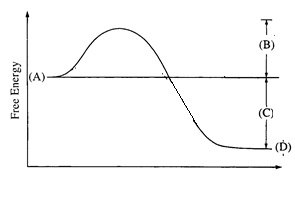 |
29. Which of these changes as a result of adding an enzyme? A B C D |
30. All of the following processes release CO2 EXCEPT
A. Krebs cycle
B. alcoholic fermentation
C. oxidative phosphorylation
D. conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
E. conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
ANSWERS
1. In thylakoid space
2. From water splitting; Proton pumps in
ETC move H+ from stroma to thylakoid space
3. NAD+
4. C6H12O6 + 6 O2
→
6CO2 + 6 CO2
5. Exact opposite
6. Red and blue-violet
7. C4
8. Corn, sugar cane
9. Photosynthesize in hot dry conditions; avoid photorespiration
10. Need more ATP than NADPH to do Calvin cycle
11. To atmosphere
12. O2, ATP, NADPH
13. B; products have more energy than reactants
14. Cells use energy released from – G reactions (like ATP
→
ADP + Pi) to power + G
reactions
15. allosteric
16. Fermentation
17. NADH = 3 ATP; FADH2 = 2 ATP
18. Glycolysis- net 2 ATP; Krebs cycle- 2 ATP; ETC- (10 NADH X3 + 2 FADH2
X 2) =34 ATP
(Plus net 2 from glycolysis + 2
from Krebs minus 2 ATP for transport = 36 total ATP/1 glucose)
19. Availability of oxygen
20. Alcoholic- bacteria make beer, wine; yeast makes bread
Lactic acid-human muscle cells
during exercise;
bacteria –yogurt,
sauerkraut, pickles
21. Needs to regenerate NAD+
22. oxygen
23. As CO2 in atmosphere
24. Citric acid cycle/tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
25. Increasing temp speeds up reaction up to a point. Too hot-denatures enzymes
26. PEP receives the C from CO2 with the help of PEP carboxylase
27. Disrupts hydrogen/ionic bonds in 2°, 3°, 4° structure
28. Magnesium (Mg)
29. B- Activation energy decreases; all others not affected
30. C. oxidative phosphorylation does NOT release CO2